Starting a nonprofit is no different from starting any other business. You need to do research, write a business plan, and file business-formation documents with your state. But nonprofits face one additional hurdle—they must get approval from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to be exempt from taxes.
This guide will help you learn how to start a nonprofit organization and will include tips for creating a nonprofit business plan so you can start on solid legal and financial footing.
1. Conduct a needs assessment
You might have a great nonprofit idea, but an idea alone isn't how you build a foundation for a charitable organization. There's also some preliminary research that needs to happen to determine if your idea is viable.
Think of it this way. A successful nonprofit fills a unique need. A needs assessment helps you identify that need, find out what other organizations are already doing, and research the best solutions.
To conduct a needs assessment:
- Visit the U.S. Census Bureau website for basic demographic information for your area.
- Talk to people at other nonprofits or businesses that have related missions. If another entity is already providing the service you want to offer, consider revising your mission or collaborating with that organization.
- Interview people who might need your nonprofit's services to find out about obstacles they face.
- Research logistics and practicalities, including federal, state, and local laws.
- Learn about similar programs in other communities.
Use this research to write a needs assessment that describes your nonprofit's mission, strengths, and weaknesses, and the need it will fill.
Remember, the main questions you're trying to answer are what is the problem, and how can my organization fix it? New nonprofits that take time to fully understand the needs they're trying to—and can—meet may be better positioned for success when it's time to launch.
2. Complete a market analysis
It wouldn't make sense to start a for-profit company without doing market research first, and the same principle applies to starting a nonprofit.
After all, organizations, including nonprofits, must bring in money to survive. That's why a market analysis—a plan for getting financial and volunteer support for your nonprofit—is a must.
Market research and analysis can help you to:
- Clarify who you would like to receive support from
- Compare your charitable organization with other organizations that serve a similar need and audience
- Refine your brand messaging and organization's mission statement
- Better understand how your nonprofit's financial situation may affect your ability to market and attract new donors or volunteers
How do you conduct this analysis when starting a nonprofit?
You can begin by listing the kinds of supporters you want, such as donors or volunteers. For each type, envision an "ideal supporter" and write down some characteristics, such as:
- Age
- Income
- Occupation
- Lifestyle
- Reasons for supporting you
Next, use surveys and interviews to reach out to potential donors to uncover their motivations for giving and the types of communications to which they respond best.
Use your research to fine-tune your ideal supporter descriptions. These descriptions will help you target your fundraising and outreach to the people most likely to be enthusiastic donors and volunteers for your cause.
Doing market research for a for-profit company typically means looking at the competition, and that's something you can do as well. For example, if there's another charitable organization in your niche that's thriving, it may benefit you to analyze how they're doing it.
The idea is not to compare but to understand:
- Who are the biggest donors?
- What strategies or tactics is the existing nonprofit in question using to raise brand awareness?
- How do the organization's goals compare to or differ from yours?
It's worth noting that you don't have to do this alone. Many companies will conduct nonprofit market research analysis for you in exchange for a fee. If your financial situation allows you to invest in something like that, it may be worth it so you have more time to focus on the other key aspects of how to start a nonprofit.
Choosing the right type of nonprofit structure is an important part of forming your nonprofit. The most common types of business structures include corporations, associations, and LLCs. For all of these structures to be recognized as tax-exempt by the IRS, they must qualify for 501(3)(c) status.
Section 501(3)(c) of the Internal Revenue Code applies federal tax-exempt status to the following entities:
- Charitable organizations
- Religious organizations
- Educational and scientific organizations
- Literary organizations
- Organizations that are focused on testing for public safety
- Organizations that foster national or international amateur sports competition
- Organizations that work toward the prevention of cruelty to children or animals
Federal law defines what is a charitable organization but gives organizers the freedom to choose which type of structure to pursue. A new nonprofit may be established as a corporation, association, or limited liability company.
Here's how they compare.
- Corporation: A nonprofit corporation is the most popular type of nonprofit organization. These types of nonprofits qualify as tax-exempt, are protected from liability, and can qualify for grants. A corporate structure could make it easier to attract donors, and you get the benefit of state tax-exempt status as well.
- Association: An unincorporated nonprofit association is when two or more people come together to benefit the public without filing legal paperwork or forming an official legal structure. If the main purpose of an unincorporated association is charitable, they can qualify as a 501(3)(c) organization.
- LLC: Forming a nonprofit LLC is similar to forming a corporation, but the organizational structure is more relaxed. Nonprofit LLCs can only be recognized as a 501(c)(3) if all of its members are 501(c)(3) organizations.
There's a fourth option as well, which is the fiscal sponsorship.
This type of arrangement can allow nonprofits to attract donors if they have not yet qualified for federal tax-exempt status as a 501(c)(3) organization. A fiscal sponsor accepts charitable contributions on behalf of the nonprofit and provides fiduciary oversight to the organization.
Choosing a fiscal sponsorship can be an opportunity to test out your nonprofit idea to see what kind of demand exists for the service(s) you're providing. You may also find it easier to outsource certain administrative tasks to a fiscal sponsor while you wait for your IRS determination letter. This letter affirms that your nonprofit meets the standards for tax-exempt status under federal law.
4. Create a business plan
A nonprofit business plan is similar to a for-profit business plan, but the fundraising section makes it different. The key elements you'll want to include in your nonprofit business plan are:
- Executive summary: This includes your mission statement and purpose, business goals, business values, and how you will meet the needs of your target audience.
- Products, services, and programs: This includes what services and programs you plan to offer.
- Community impact: Think about how the programs and services you're offering will impact the community and how you'll measure your success.
- Market and competitive analysis: Determine any gaps in your market, how your nonprofit will help fill those gaps, and your plan for getting support.
- Organizational structure and staffing: This includes how your business will operate and what employee roles you'll need to fill to execute day-to-day operations.
- Marketing plan: This should include your target market (potential donors) and your plan for recruiting and getting people involved in your mission.
- Financial plan: This includes how you plan to get funding—including grants and donations—to operate your nonprofit.
A well-written business plan is something most nonprofits can benefit from having. Similar to the way a for-profit business might use its business plan to obtain loans or other types of financing, you might use your plan to attract individual and institutional donors.
Keep in mind that as your organization grows, you may need to revisit your business plan and make adjustments to it. If your organization's mission changes, for instance, or you decide to expand the scope of services you offer, you'd want to integrate those things into your plan.
5. Secure funding
When starting your nonprofit organization, you may need a hefty amount of funding upfront to cover startup costs, as well as continuous funding to bring in revenue and help you sustain your organization.
When looking for funding options, grants, donations, and membership programs are some of the most popular ways nonprofits generate operational funds.
Grants
There are many different types of government grants available to nonprofits to help with startup funding—available at local, state, and federal levels. The application process is often extensive.
Below are the steps you can take to secure a grant for your nonprofit:
- Search for a grant that could be a good fit via Grants.gov
- Review the grant requirements
- Determine your eligibility
- Fill out the application
- Review the application requirements
- Submit your application
Donations and fundraising
Donations can come in a variety of ways, including corporate sponsorships, individual donations, and events.
- Corporate sponsorships: These donations are made by larger corporations who are interested in your nonprofit's mission.
- Individual donations: These donations are individual donations made on a one-time or recurring basis, usually made online or in person at events.
- Fundraising events: Events are a great way to generate funding and raise awareness for your organization.
Be careful about fundraising before receiving your 501(c)(3) status. If your application is denied for any reason, your donors won’t be able to take that deduction and the negative press is risky for a new nonprofit.
Membership programs
Part of keeping your nonprofit running is by having a membership program in which members can contribute money to your organization. This usually includes a membership fee—whether a one-time, yearly, or monthly fee—that can help with running costs.
These fees usually result in membership benefits, like free entry to fundraising events, access to a member newsletter, and discounts to local businesses. Membership organizations can be an effective way to raise funds while ensuring that donors remain engaged with your organization.
Nonprofits typically pursue fundraising through multiple avenues rather than limiting themselves to just one option. Looking at how other charitable organizations in your niche are raising funds can give you a better idea of which methods are most effective.
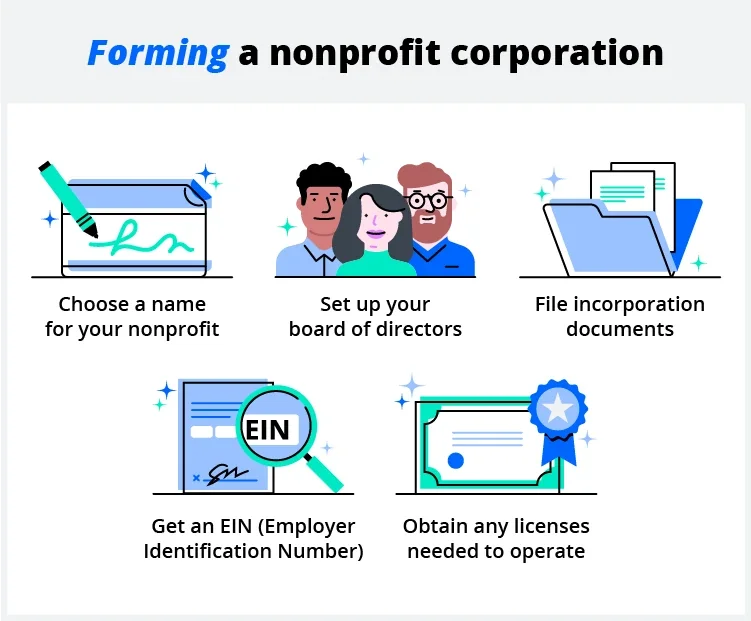
6. Form your nonprofit
Once you've built a solid foundation and have secured funding, it's time to form your nonprofit business. When forming a nonprofit corporation, you'll have to:
- Choose a nonprofit name
- Set up a board of directors
- File incorporation documents
- Create bylaws and operating rules
- Get an employer identification number (EIN)
- Obtain any licenses
Keep in mind that most states have a special business classification for nonprofit corporations. If you plan on receiving donations from another state, you'll also have to register there. The National Association of State Charity Officials (NASCO) is a great resource for finding contact information for the state you'd like to register in.
Nonprofit incorporation or LLC: What's the difference?
Part of forming your nonprofit is choosing your legal structure. In most cases, nonprofits are formed as corporations, but an LLC can also be a nonprofit. A nonprofit incorporation and a nonprofit LLC will both have the same purpose—to serve a community.
Those forming a new nonprofit may be interested in an LLC structure because it can be more flexible with its organizational structure. A nonprofit corporation, on the other hand, has more restrictions when it comes to shareholders, directors, and managers.
The biggest difference between forming a nonprofit incorporation and a nonprofit LLC is the requirements involved in the process.
Forming a nonprofit corporation includes all of the steps mentioned above. However, there are a few additional and more complicated steps when forming a nonprofit LLC, one of which is obtaining 501(c)(3) status so you can qualify for tax exemption.
For a nonprofit LLC to be recognized as tax-exempt, it must:
- Be owned by a sole member that is a 501(c)(3) organization
- Be owned by two or more members that are both organizations or
- File Form 1023 with the IRS to apply to be recognized as tax-exempt under section 501(c)(3)
It's important to consult any state laws affecting the formation of a nonprofit corporation or LLC. For instance, state law may specify:
- How many board members you must have on the board of directors if one is required for your organizational structure
- The duties and responsibilities of the executive director, if you're required to appoint one
- How often board meetings must be held
- When and how the details of board meetings must be disclosed to the public
It's important to ensure your nonprofit complies not only with federal law but state law as well to avoid fines or other penalties.
7. Apply for tax-exempt status
Once you've incorporated your nonprofit, you'll want to apply for tax exemption with the IRS. Remember, you must have an employer identification number before submitting your application.
Each of the many types of nonprofit organizations has rules for tax-exempt eligibility, tax-deductibility of contributions, and whether the organization can lobby legislators or support candidates.
Most nonprofits are 501(c)(3) charitable organizations. Of those, most are public charities—a category that includes animal welfare organizations, food banks, and museums. Private foundations are also 501(c)(3) organizations.
Donations to 501(c)(3) organizations are tax-deductible, and income that fulfills their mission is exempt from taxes.
To get tax-exempt status, you'll need to download, complete, and submit the appropriate IRS application.
- Form 1023 is for large nonprofits
- Form 1023-EZ is for smaller organizations
After you file your nonprofit application, the IRS may have questions or need more information. If everything is in order, it can still take several months to receive a determination letter granting tax-exempt status.
Once you receive your IRS determination letter, you can file for tax-exempt status in your state. Keep in mind that you may also need to apply for sales tax exempt status or property tax exemptions separately from corporation registration. The requirements for state tax forms can vary based on where you're located.
Be aware that the IRS requires 501(c)(3) organizations to pass a public support test to qualify as tax-exempt charities. The public support test measures how much of a charitable organization's donations come from public donors.
There are two standards used to test for public support. One is for charitable organizations described in sections 509(a)(1) and 170(b)(1)(A)(vi) of the Internal Revenue Code. The other is for organizations described in section 509(a)(2).
- The 509(a)(1) test requires that a nonprofit organization receives at least one-third of its support from contributions from the general public or meets the 10% facts and circumstances test.
- The 509(a)(2) test requires that the organization receive more than one-third of its support from contributions from the general public and/or gross receipts from activities related to its tax-exempt purposes.
Under the second test, nonprofits can receive only one-third of support from gross investment income and unrelated business taxable income.
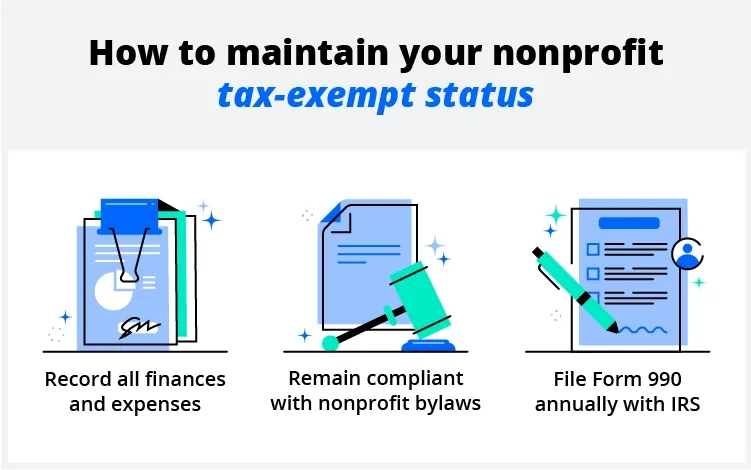
8. Keep your tax-exempt status
The final step in starting a nonprofit organization is maintaining your tax-exempt status. Here are the things you need to do to keep your tax-exempt status year-round:
- Keep detailed records and documentation: You'll need to keep a record of all donations, grants, and funding you've received, operational expenses, and all financial records. You'll use these records to prove that your revenue is going toward the purpose you intended.
- Stay compliant with bylaws: Nonprofit bylaws include all of the guidelines and laws you must follow to operate your nonprofit. It's important to ensure you're always adhering to these laws and using them to make all important operational decisions as a part of maintaining your tax-exempt status.
- File your annual tax forms: If your annual revenue is over $50,000, you must file Form 990, and if your annual revenue is below $50,000, you must file Form 990-EZ.
-
Observe other annual reporting requirements. Your state may also require you to file additional paperwork to submit with your Form 990. You may also be required to periodically renew your state tax-exempt status or update your organization's information.
The IRS can audit charities and nonprofits the same way they can for-profit businesses or individual taxpayers. That's why it's so important to keep accurate records of your financial situation. Some of the financial statements you should maintain include:
- Statement of Activities (Income statement)
- Statement of Financial Position (Balance sheet)
- Statement of Functional Expenses
- Statement of Cash Flow
If you haven't established a separate bank account for your nonprofit, that's something you'll need to do. There are banks that offer nonprofit banking packages that operate similarly to business bank accounts. Using accounting software for nonprofits that integrates with your bank account can make it easier to generate the necessary financial statements for your organization.
Starting a nonprofit FAQ
Can anyone start a nonprofit?
Starting a nonprofit requires dedication, commitment, time, and financial resources. It also helps to have some local expertise with the need that you're trying to meet. However, there's no rule that says you must have a certain degree or professional background to start a nonprofit.
If you're thinking of starting a nonprofit, it's important to be realistic about what the process involves and how committed you are to furthering your cause. Resilience and determination are important qualities to possess, as most nonprofits encounter some initial bumps along the way.
How do I start a nonprofit organization with no money?
If you're trying to start a nonprofit organization with no money, government grants and loans may be available to help with startup costs. Fiscal sponsorships are also another great way to get your nonprofit up and running.
Fiscal sponsorships can be formed when community organizations or other nonprofits partner with new nonprofit organizations. Through this partnership, you can receive help attracting donors and securing funding before your nonprofit is recognized as a 501(c)(3) by the IRS. Aside from funding, a fiscal sponsor can help guide you through the process of starting your nonprofit and help tackle administrative tasks.
How do nonprofit owners make money?
Nonprofits receive their revenue through things like grants, donations, and membership programs. They then use their revenue to pay for expenses needed to operate their business—including employee salaries and compensation.
Nonprofit owners pay themselves (and their employees) a fair salary from the revenue they receive, as it is an operating business expense.
Can you start a nonprofit alone?
The short answer is yes—you can start a nonprofit organization alone. However, a lot of time and effort is involved in the startup process, and having support from a partner or team can help make things run more smoothly. You'll also need to form your board of directors that will be involved in important decision-making, so you'll eventually need a team by your side.
If you have questions about how to start a nonprofit, there are resources that can help. The National Council of Nonprofits, for instance, provides information and guidance on starting a nonprofit. Talking to an experienced attorney can also help you gain clarity about what's involved in the process.
What is the easiest nonprofit to start?
The easiest type of nonprofit to start is one that has low startup costs and can easily attract donors or volunteers to support your mission. Ideally, it also aligns with a need you're hoping to fill in your community. Examples of simple charitable organizations to start can include literary organizations or a community garden that encourages hands-on participation.
Is it better to start a nonprofit or for-profit?
Nonprofit organizations and for-profit businesses are two different wheelhouses. Simply put, a for-profit business's main purpose is to make a profit, while the purpose of a nonprofit is to use its profits to give back to a community and further its mission. Because of this, nonprofits are exempt from paying taxes, and for-profit businesses must pay taxes by law.
Choosing between the two all comes down to your business goals.
If your main goal is to sell products or services to make money, a for-profit business may be for you.
If your main goal is to have a charitable business that gives back to the community, a nonprofit business may be for you.
Start your nonprofit today
Setting up a nonprofit can be complicated and time-consuming, but consulting a lawyer who has experience with nonprofits can help the process go smoothly. A lawyer can answer questions, prepare articles of incorporation, and review your application to the IRS. They can also explain your ongoing obligations so you can maintain your tax-exempt status and continue to run a successful nonprofit organization.